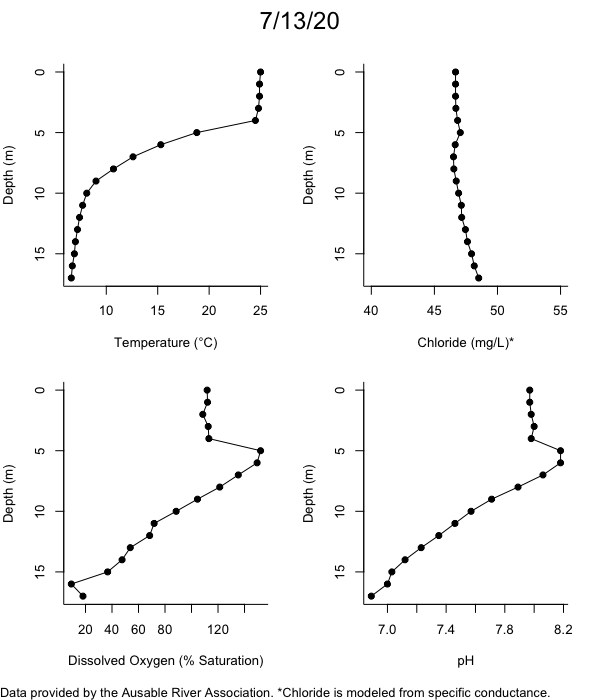
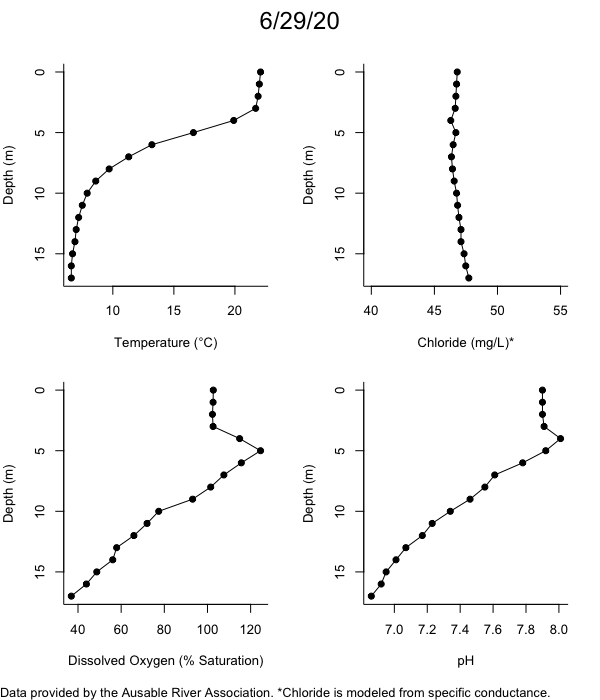
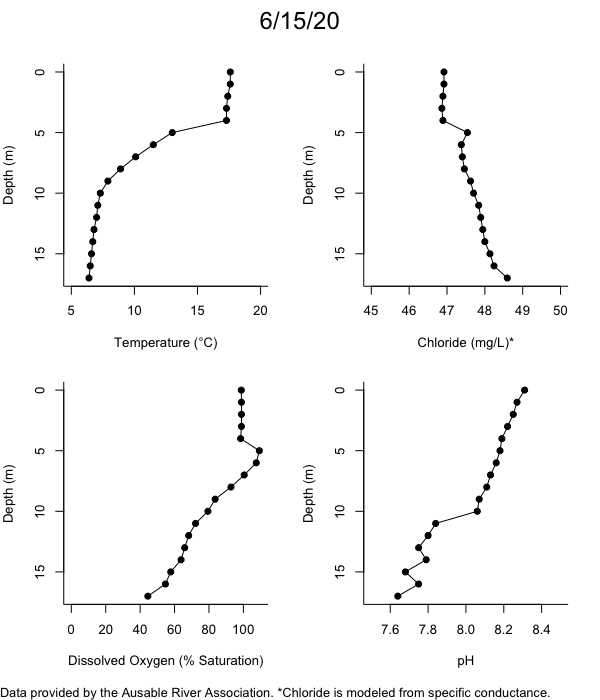
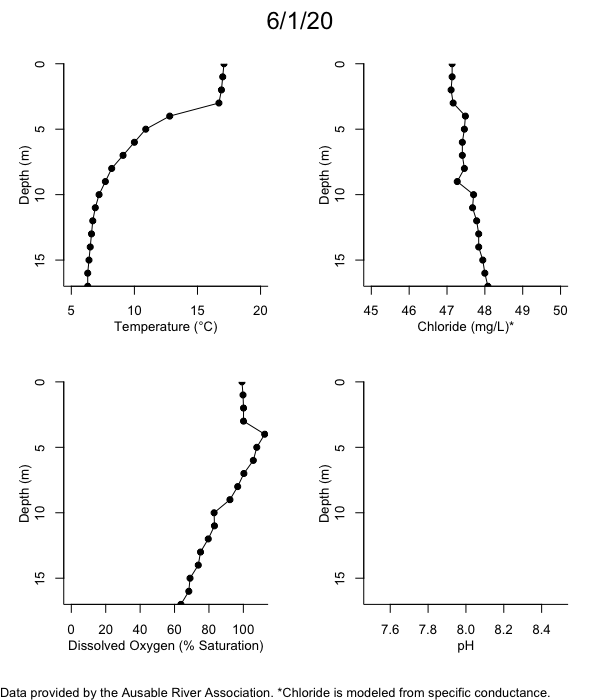
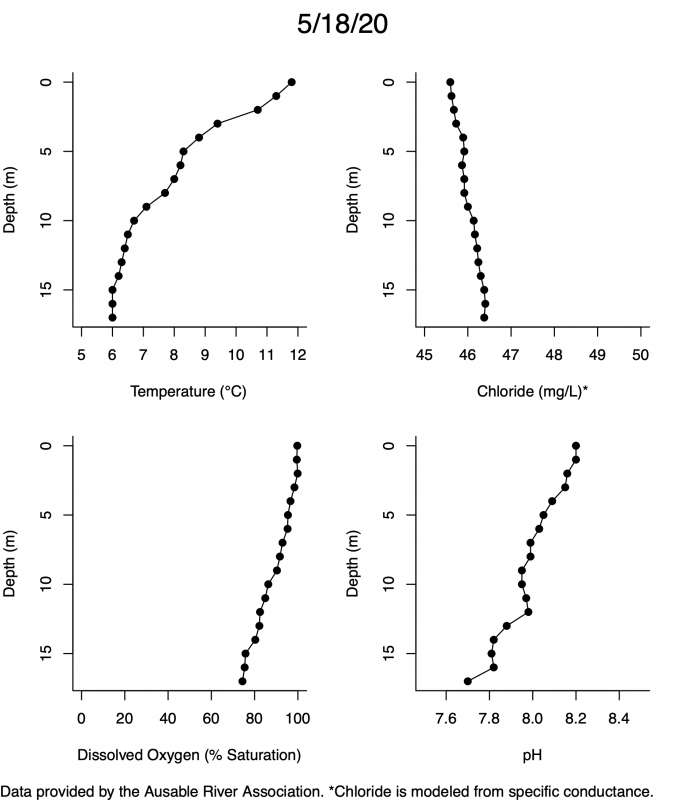
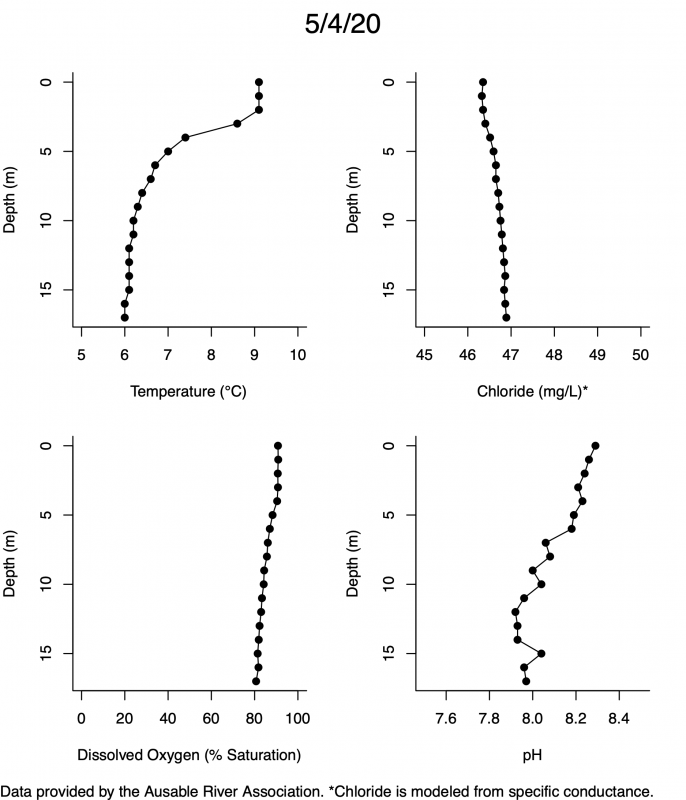
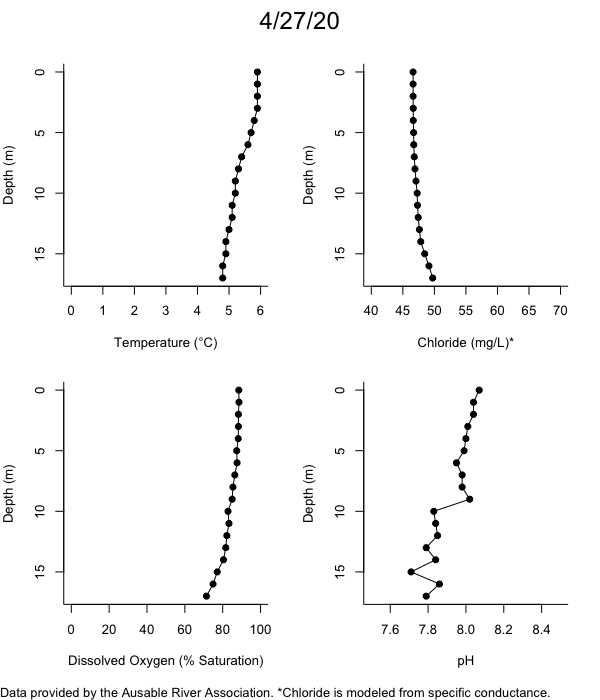
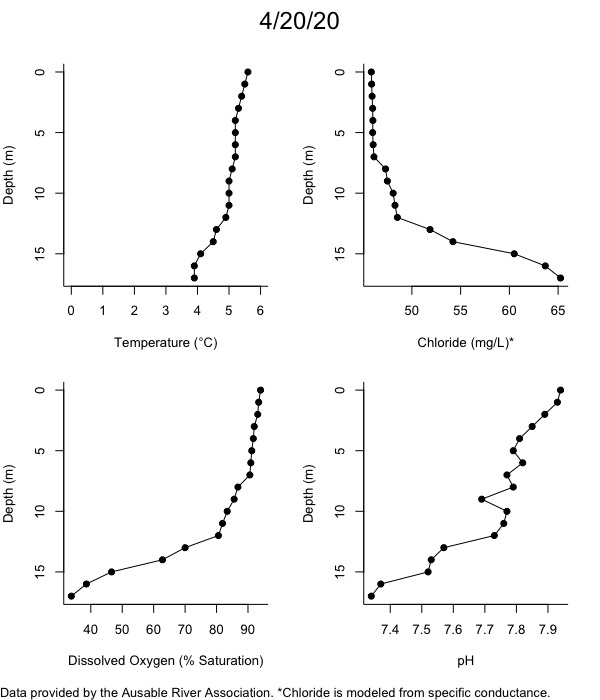
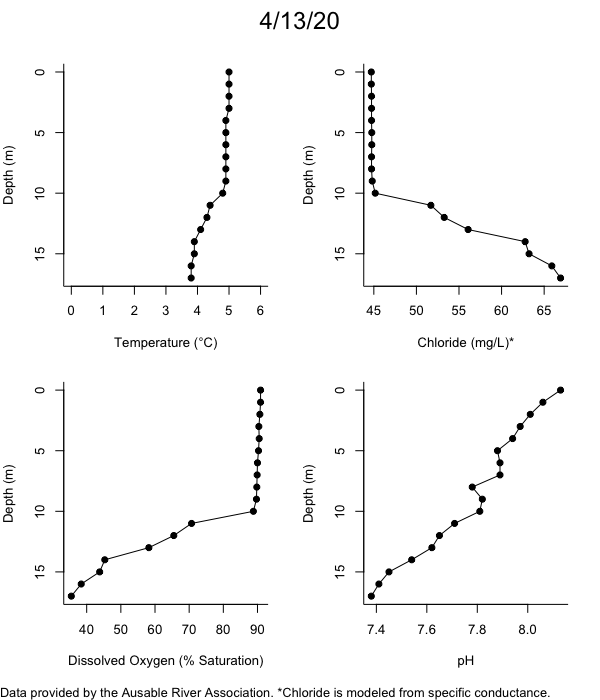
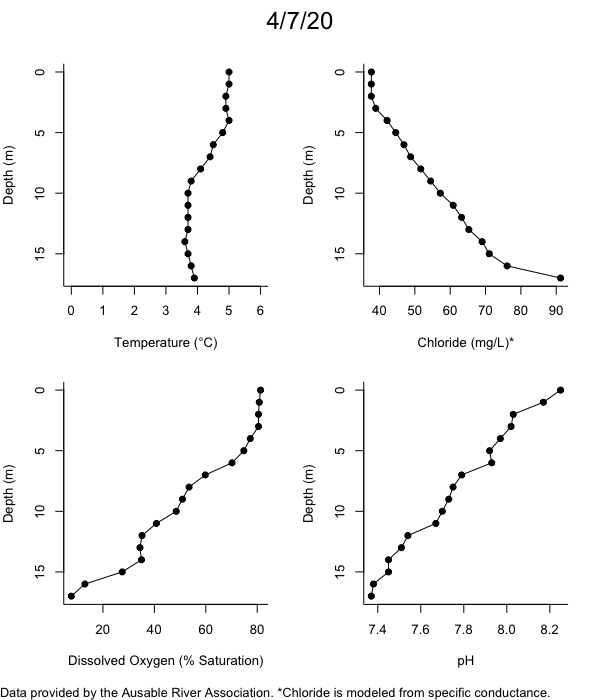
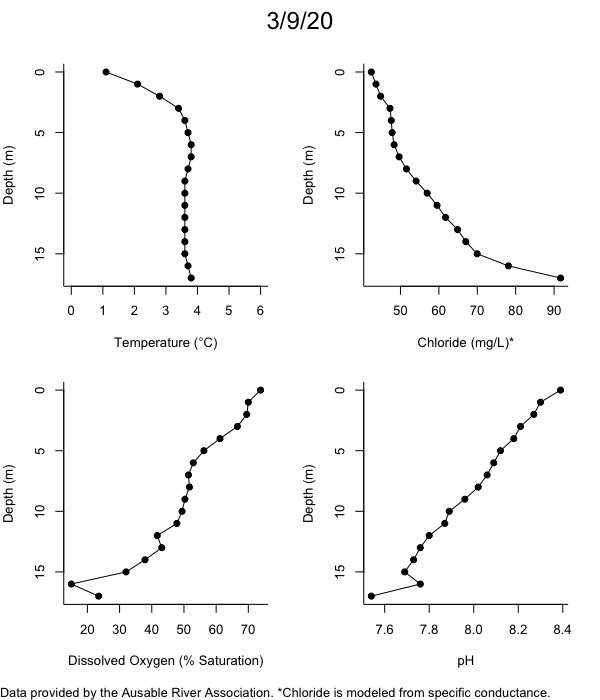
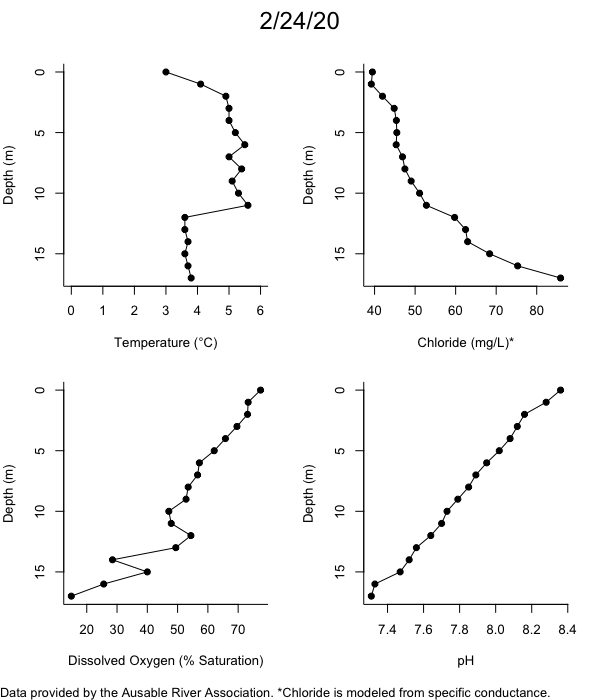
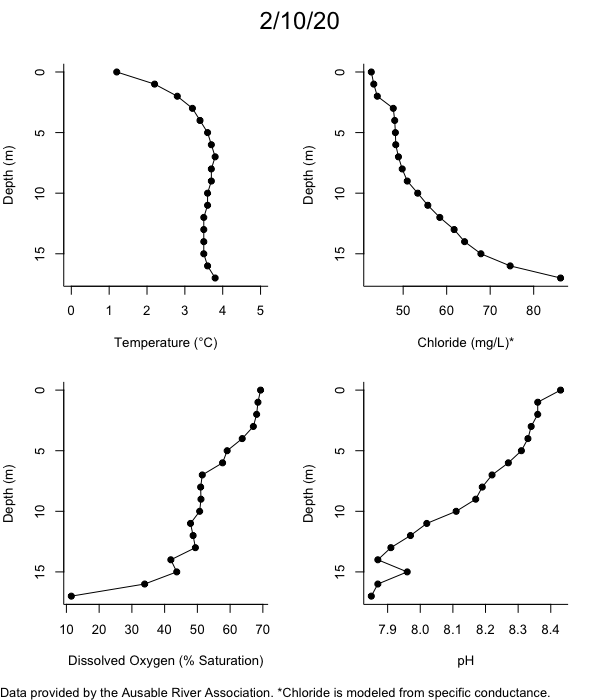
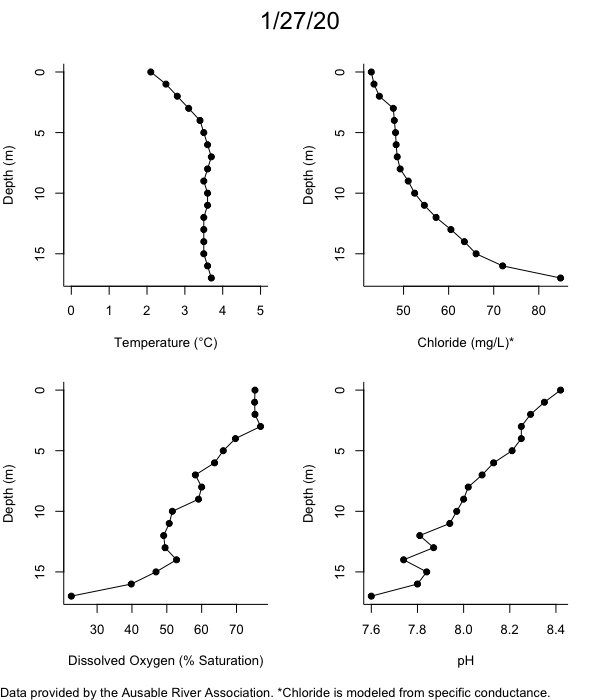
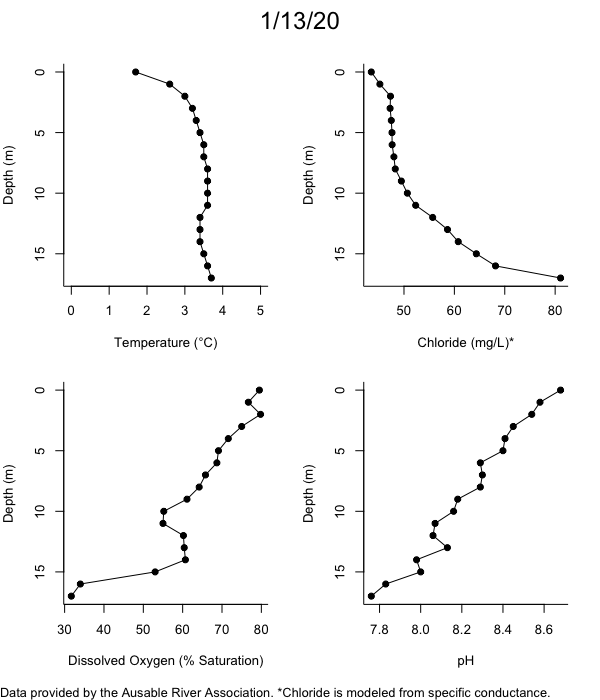
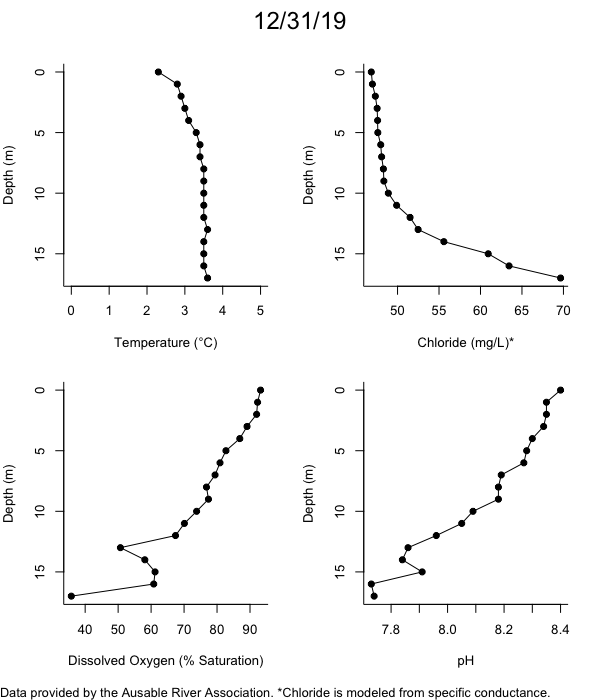
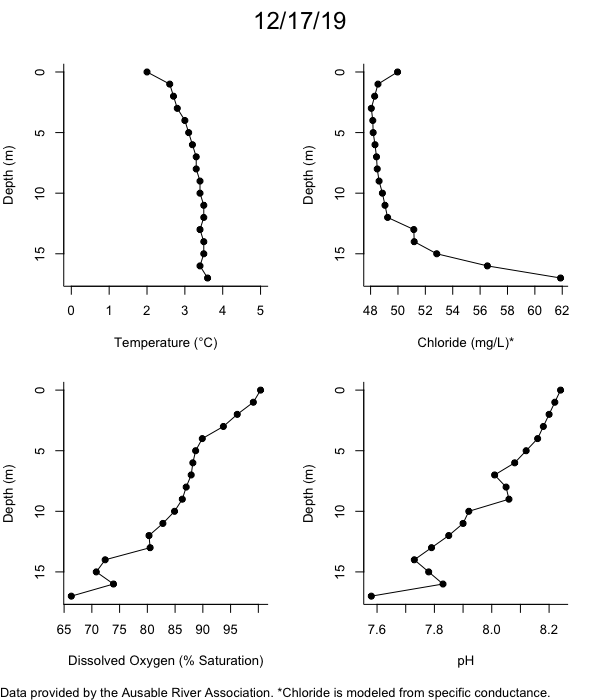
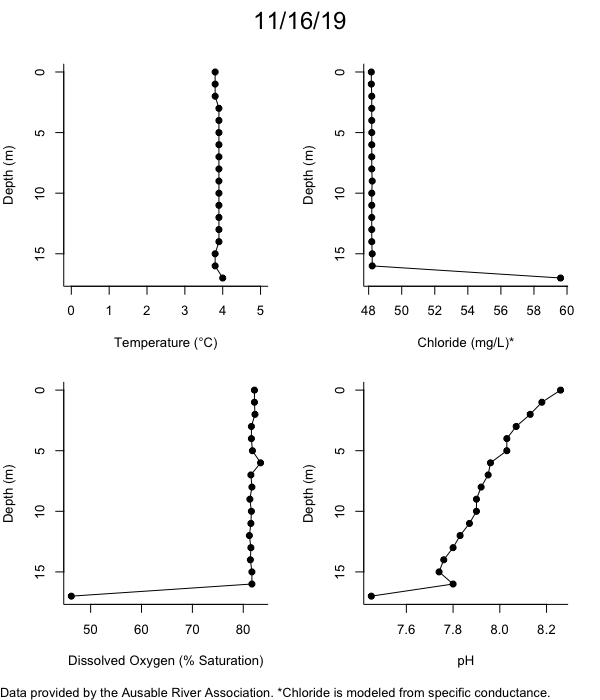
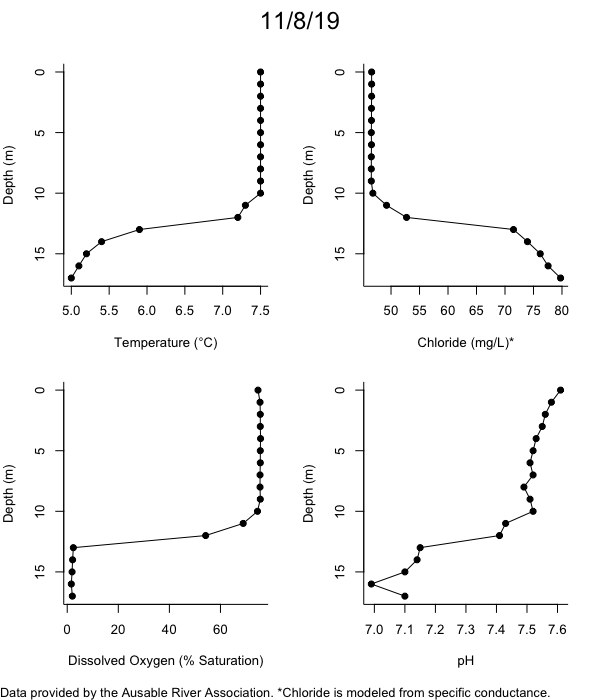
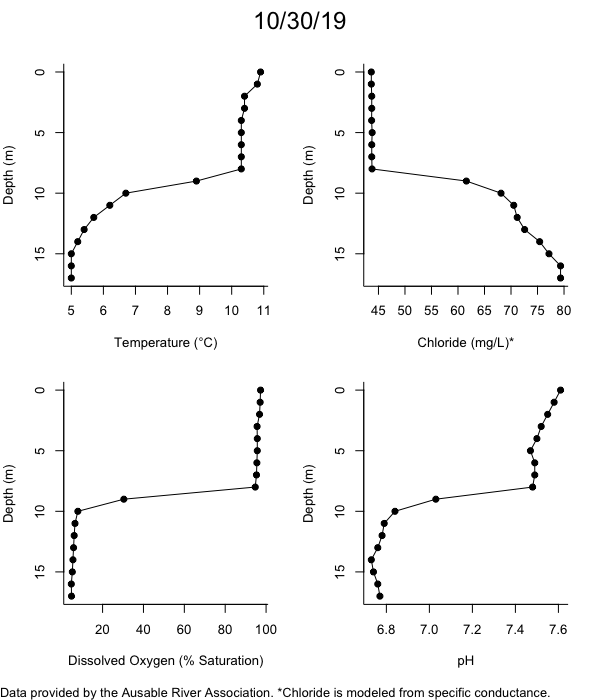
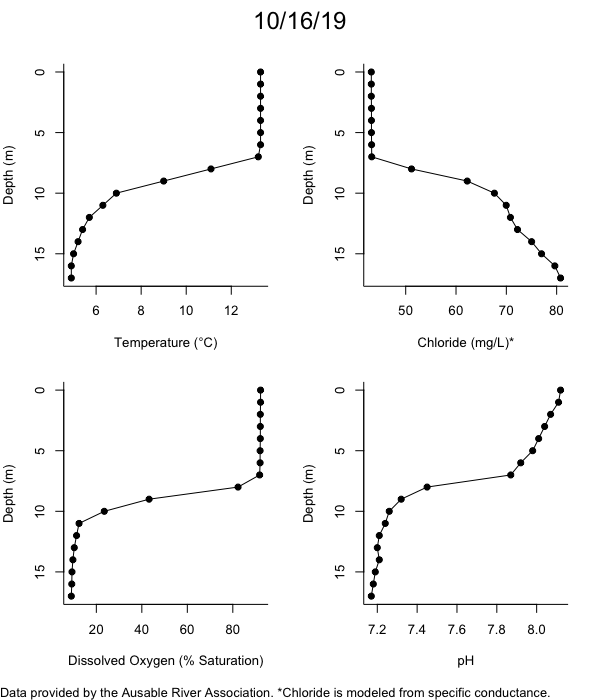
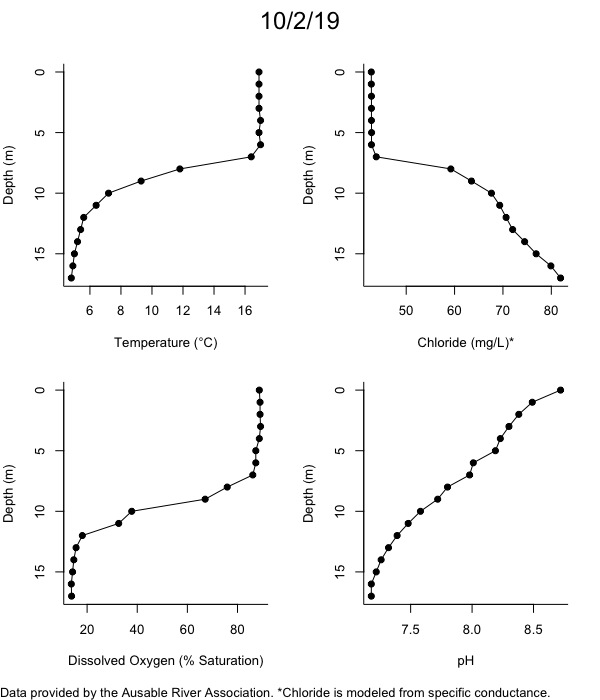
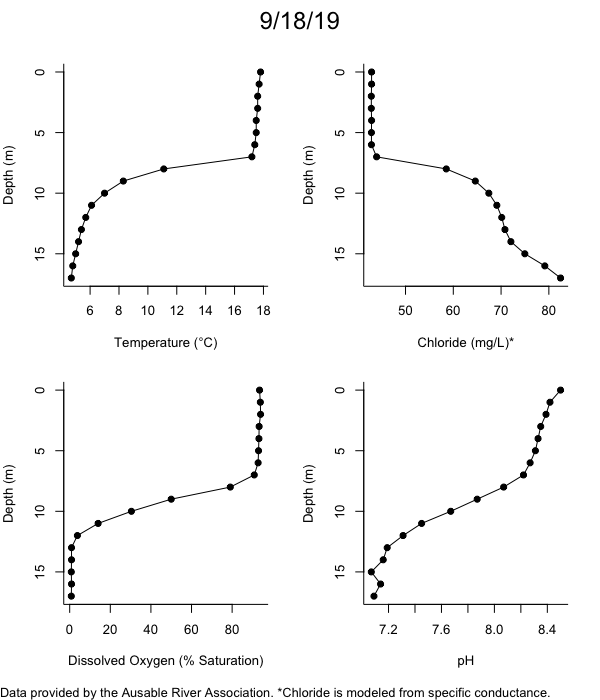
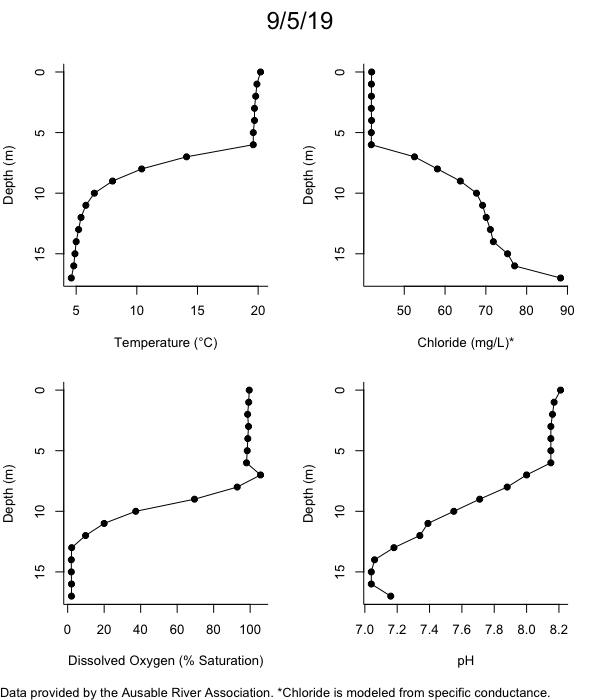
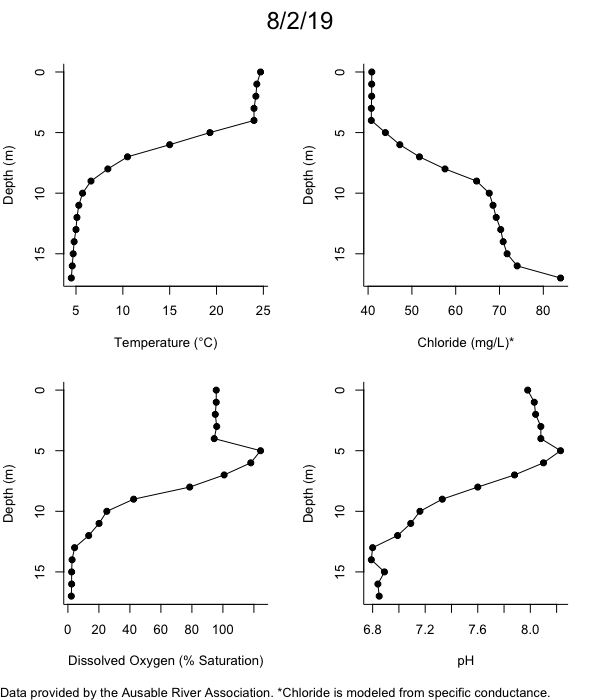
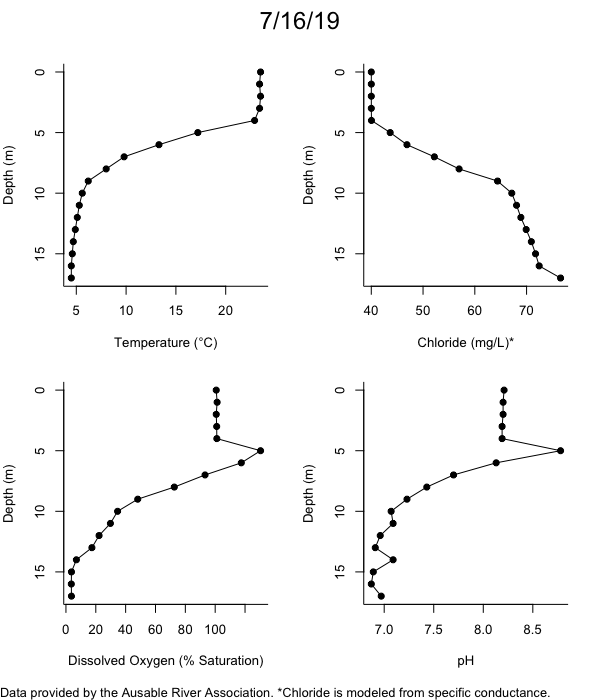
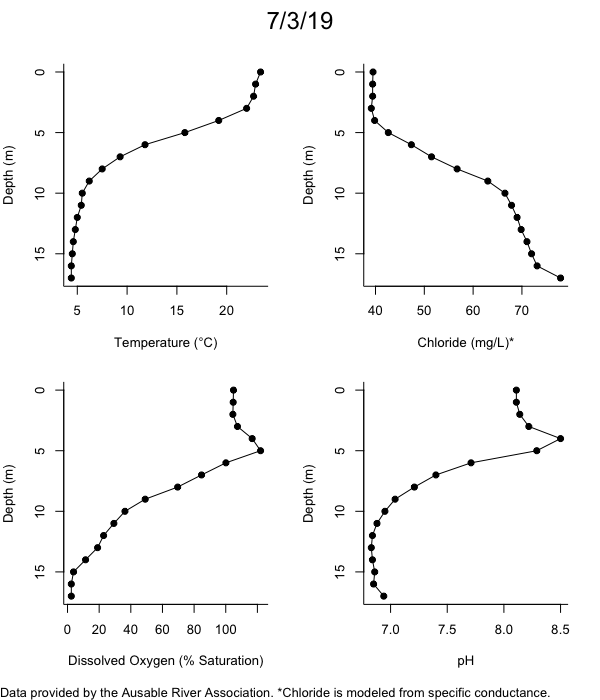
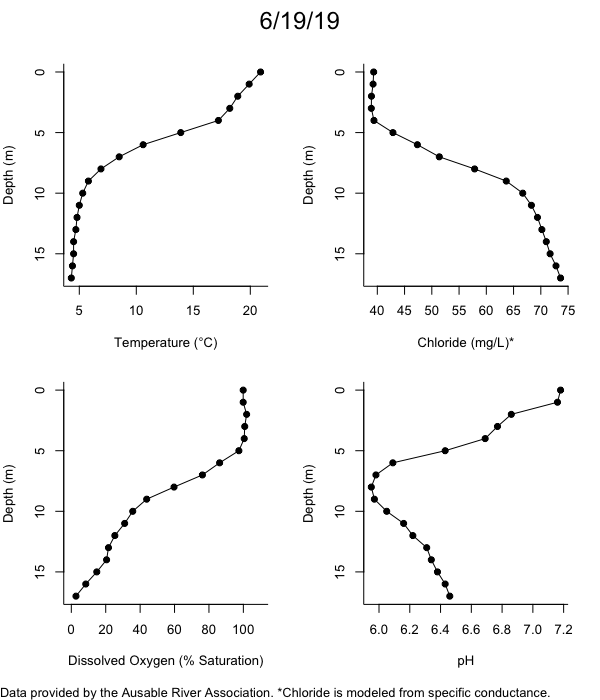
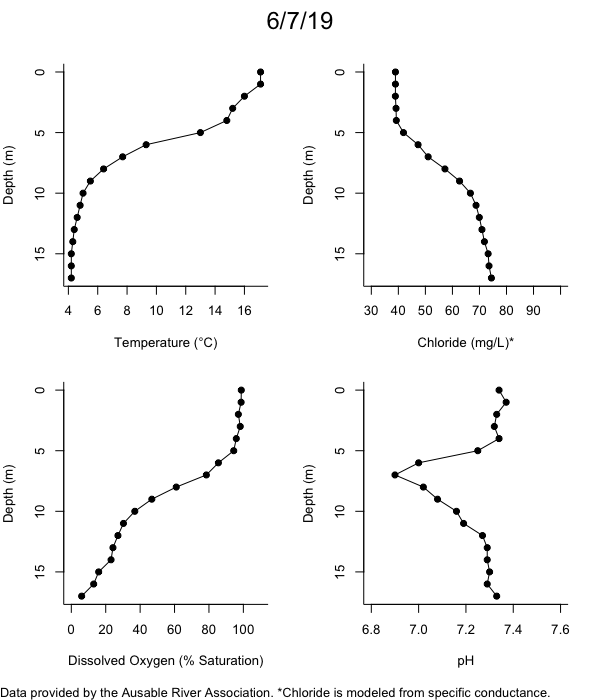
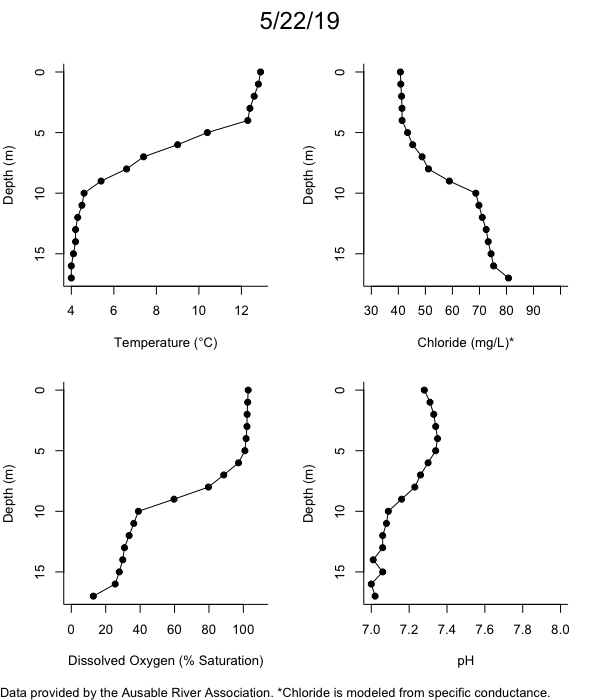
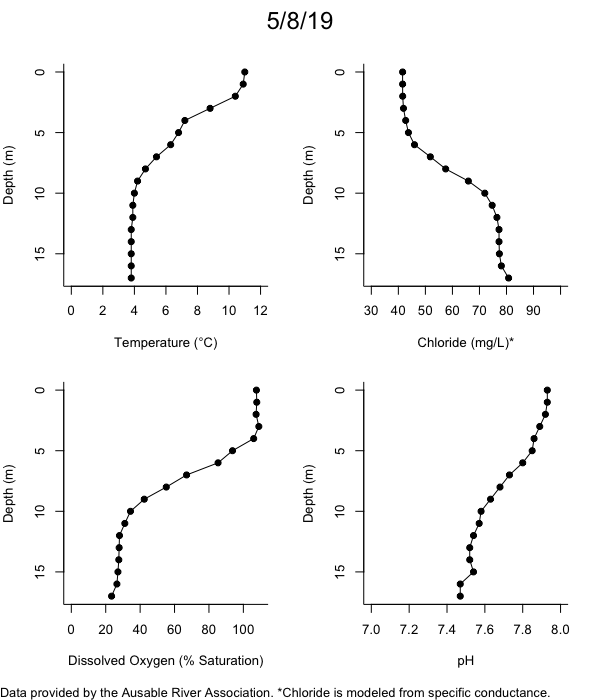
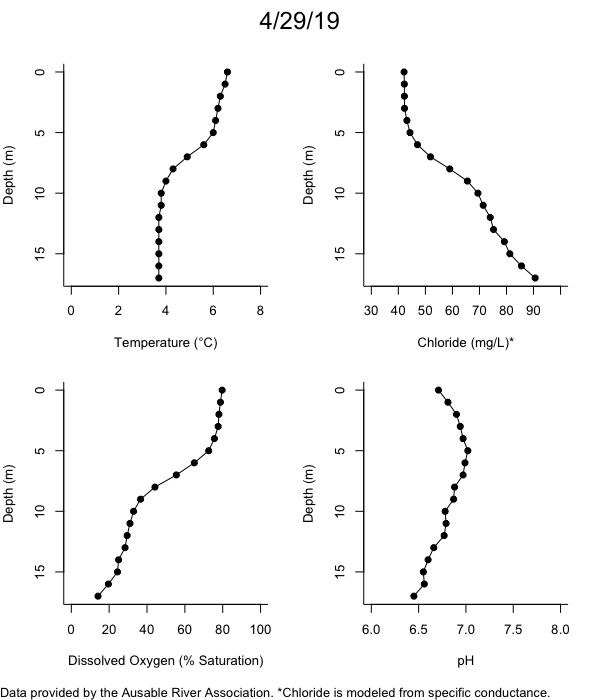
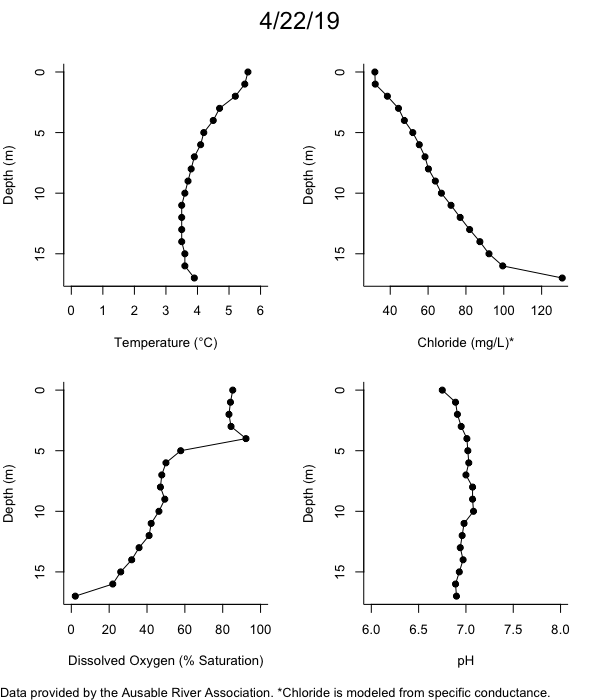
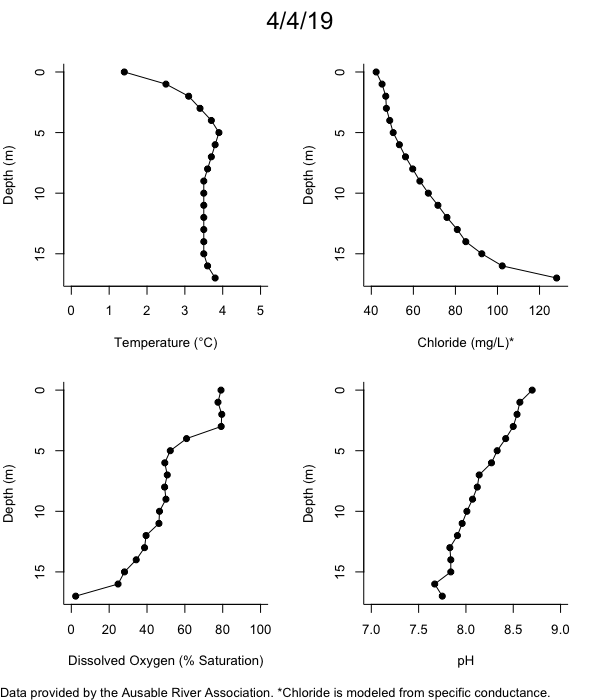
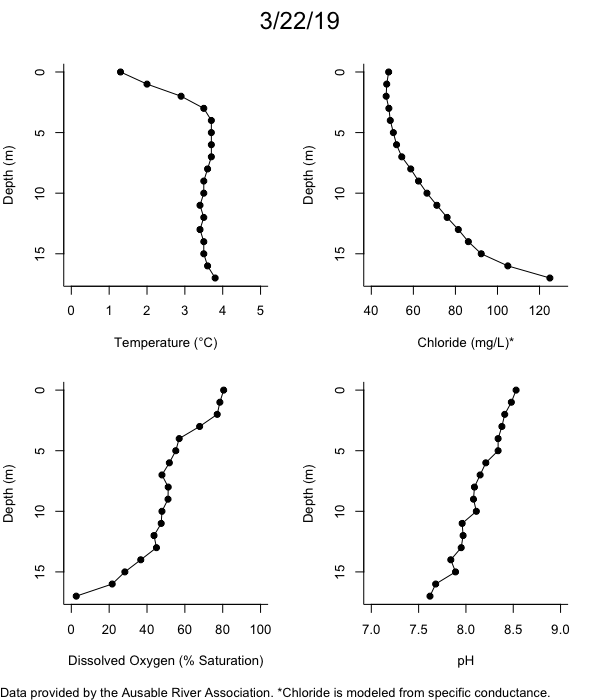
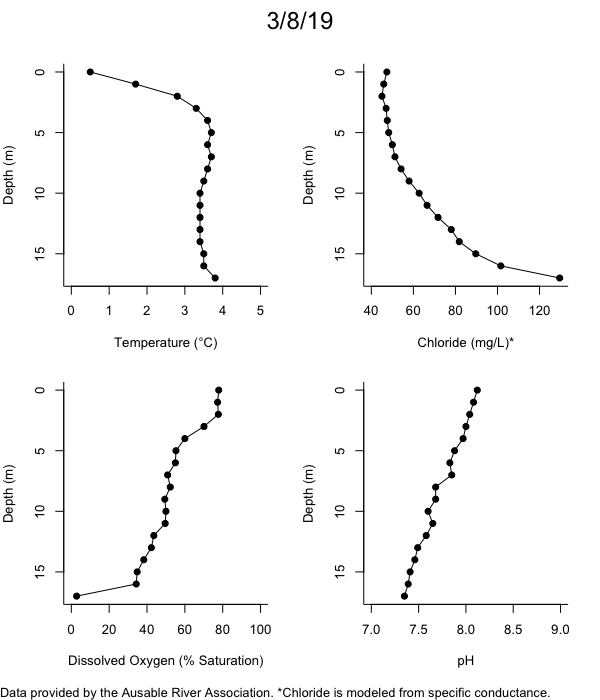
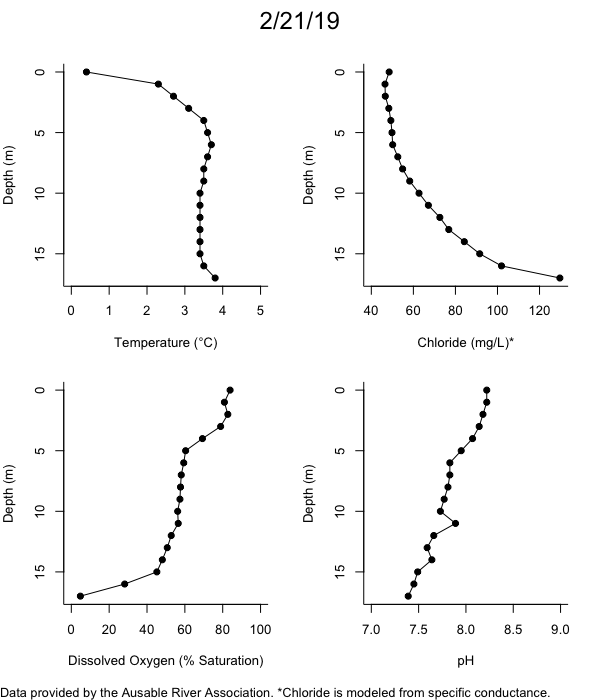
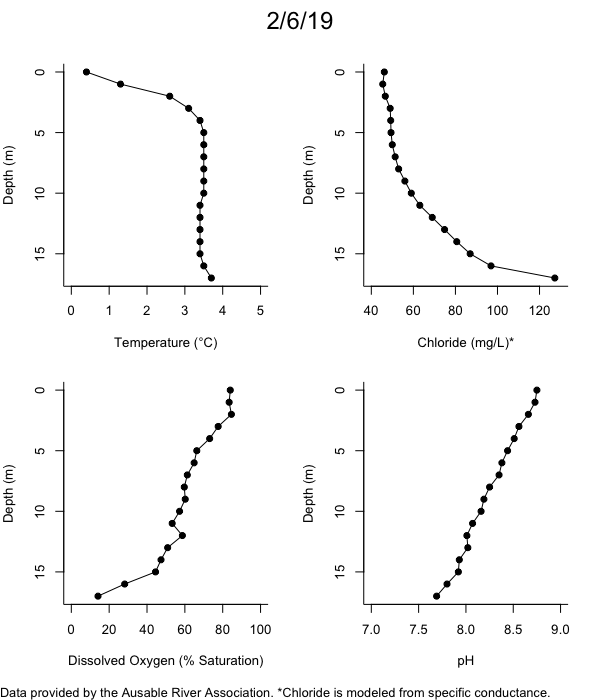
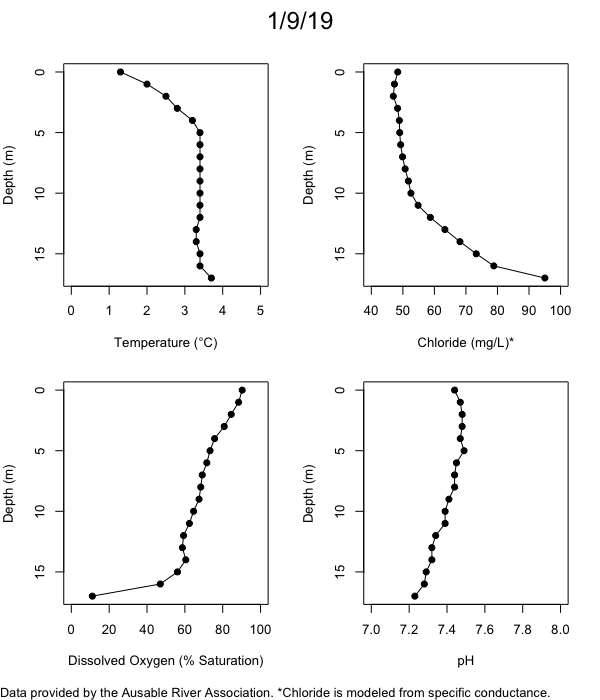
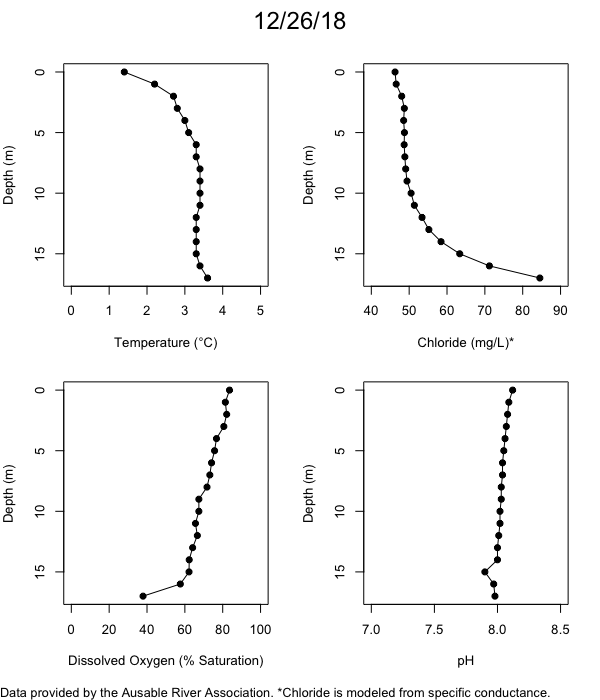
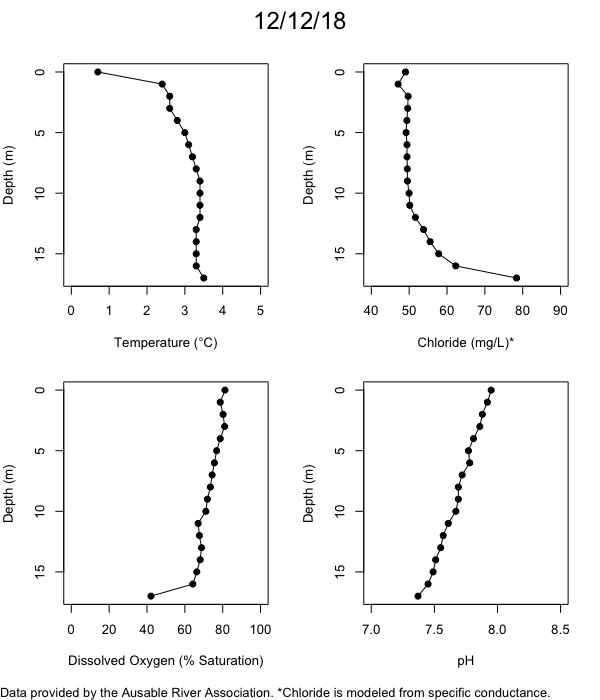
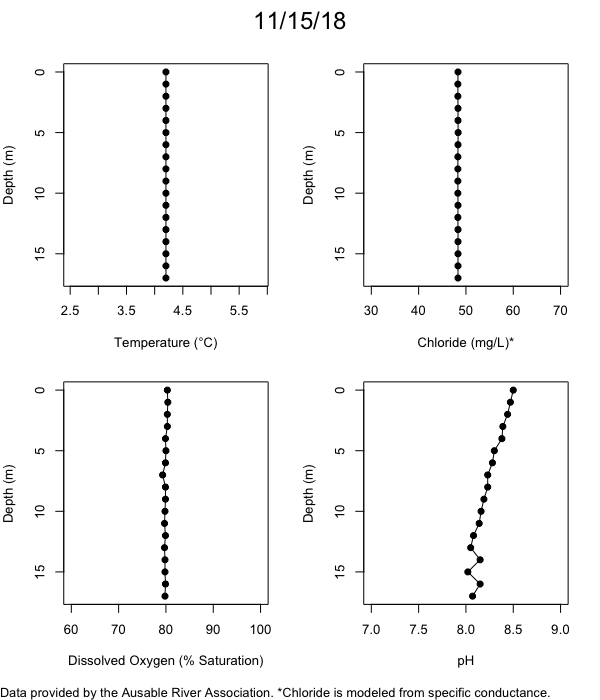
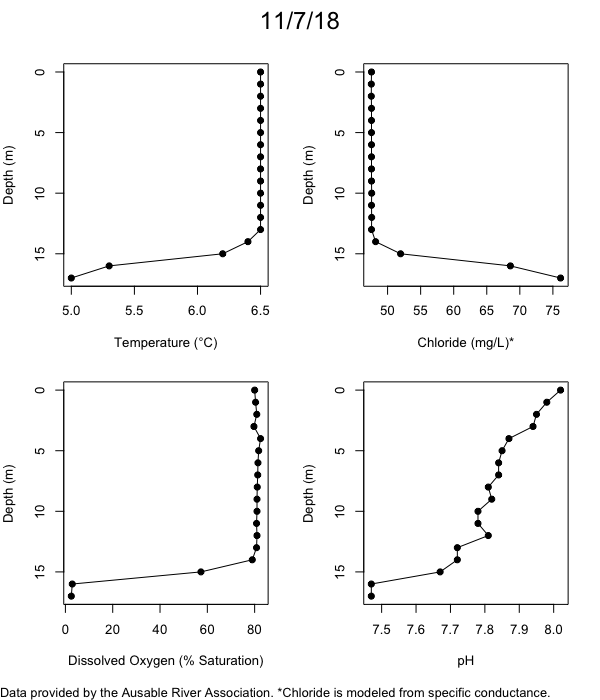
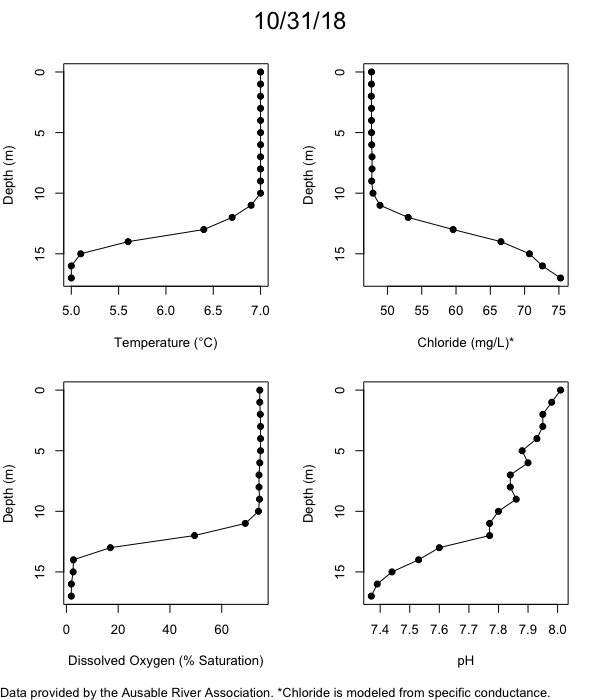
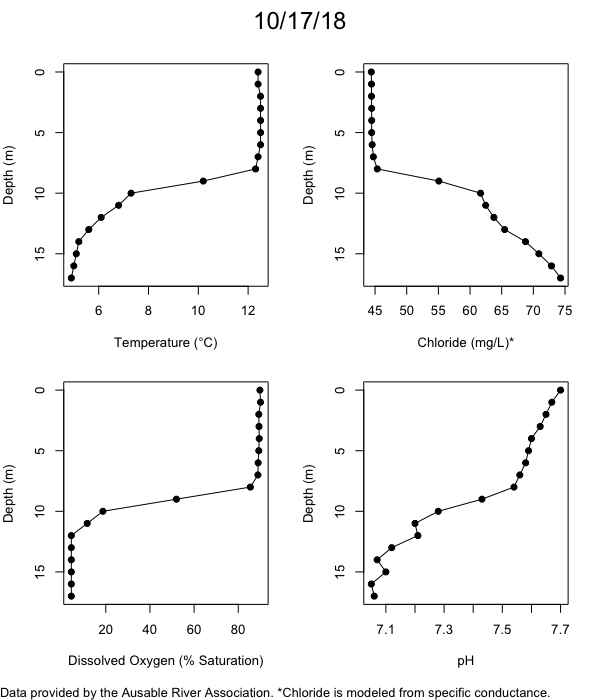
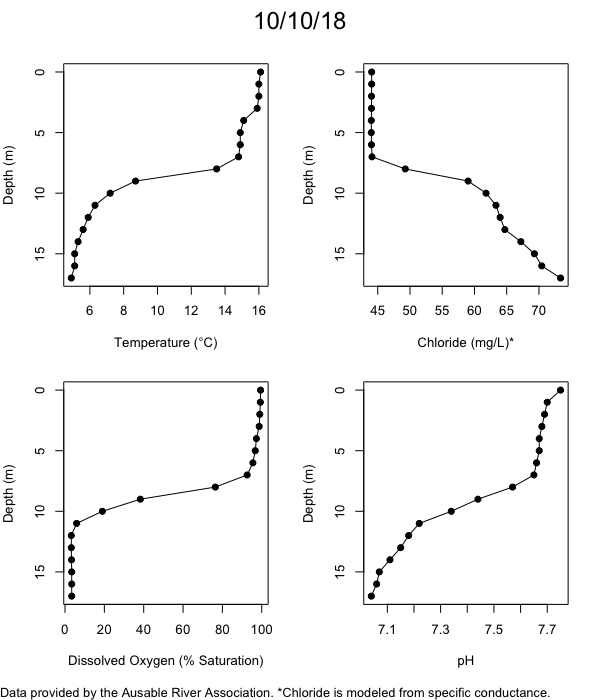
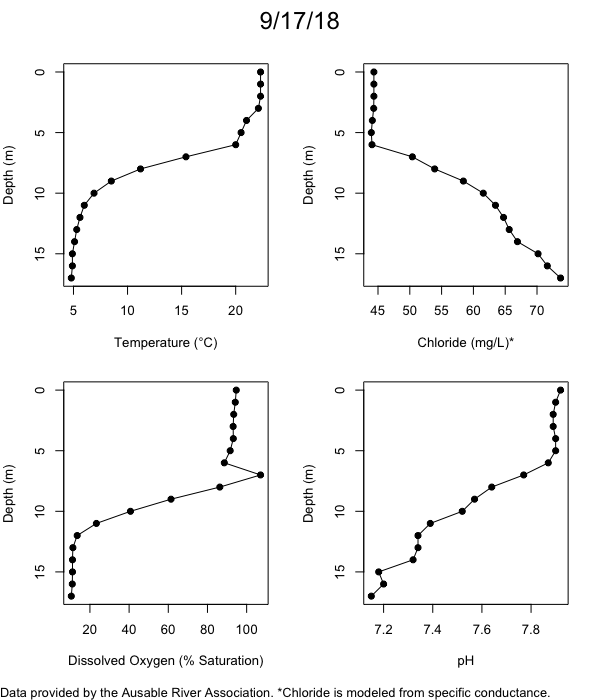
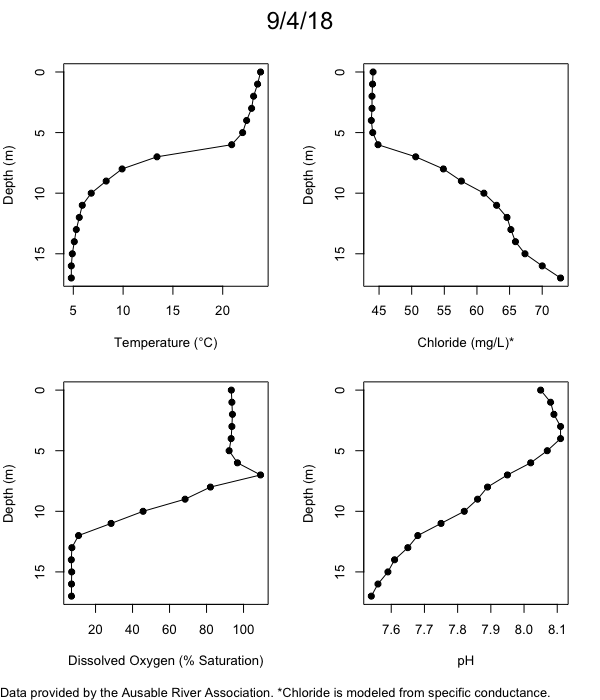
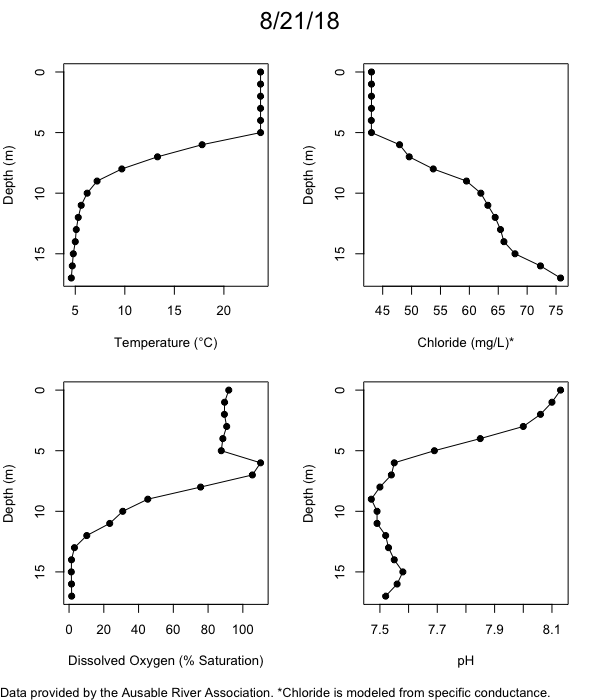
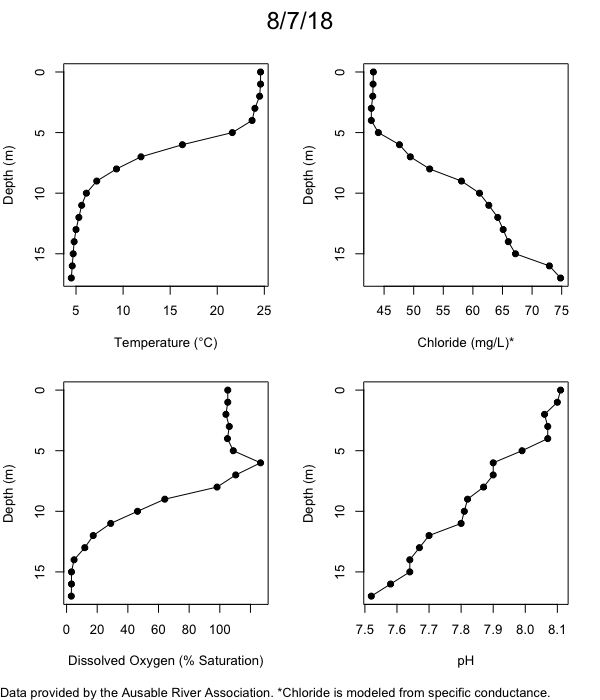
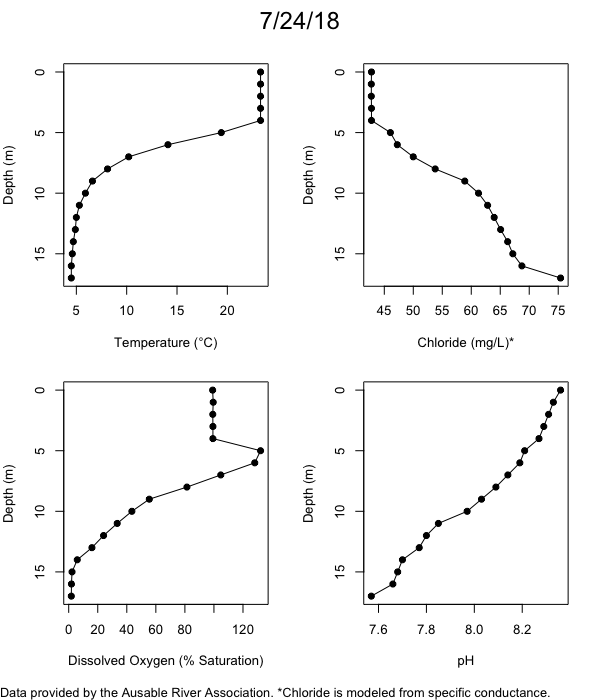
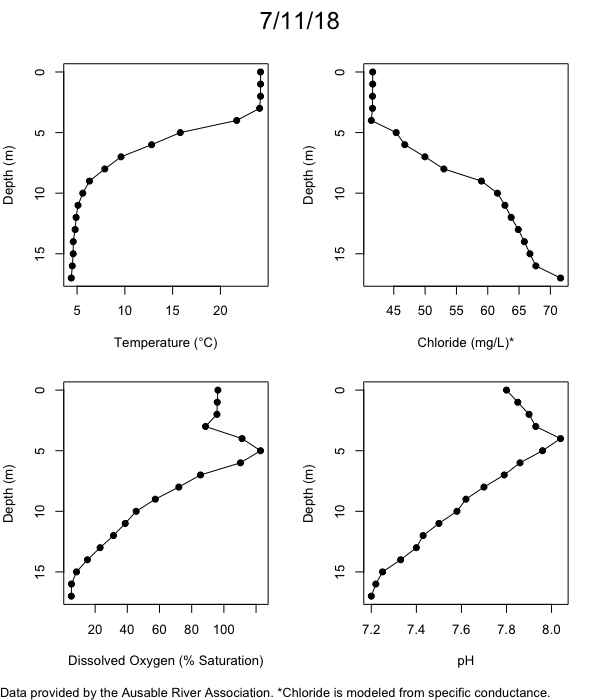
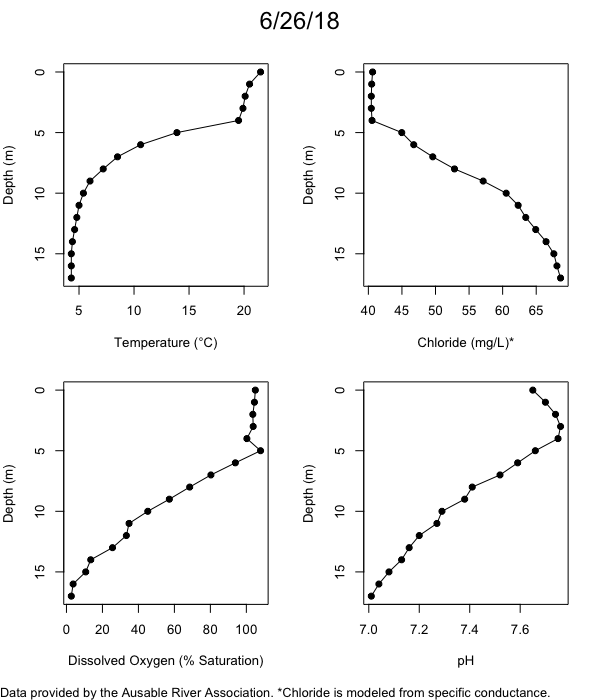
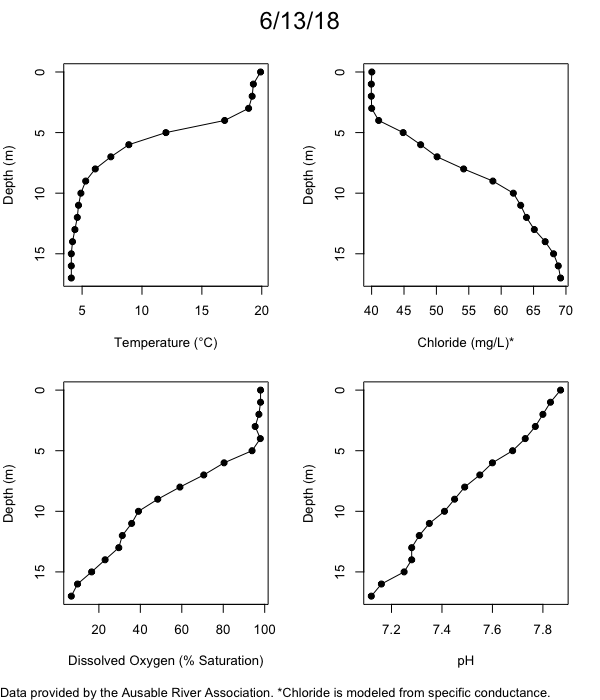
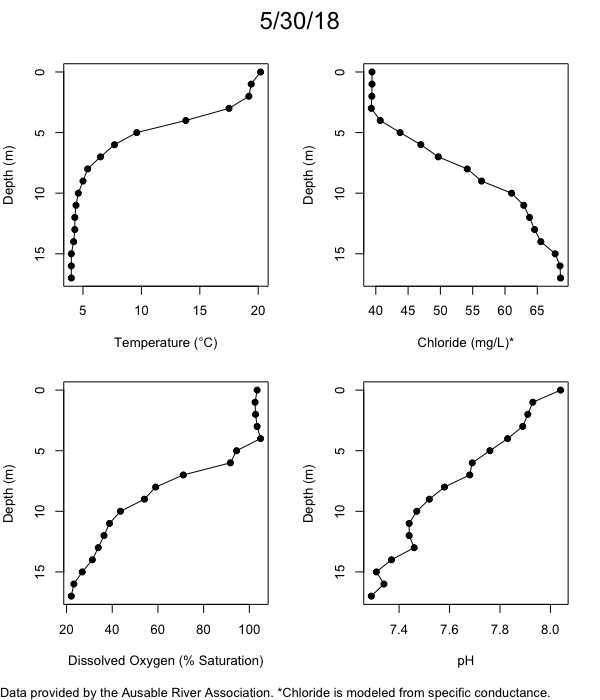
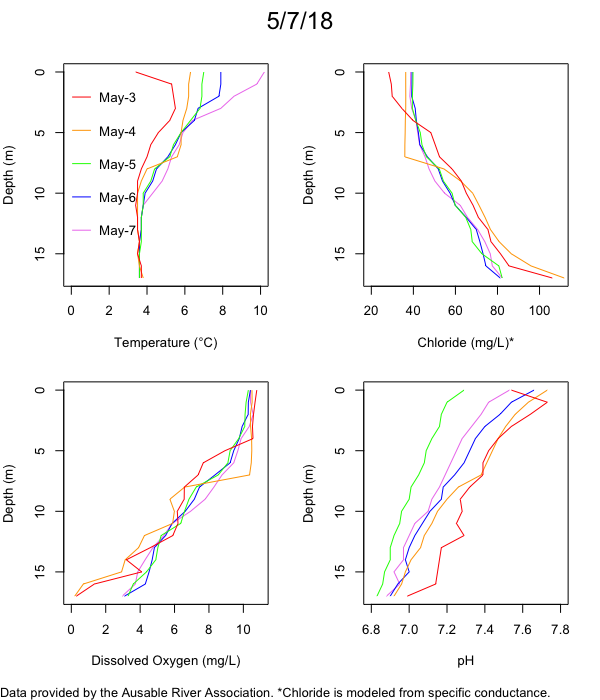
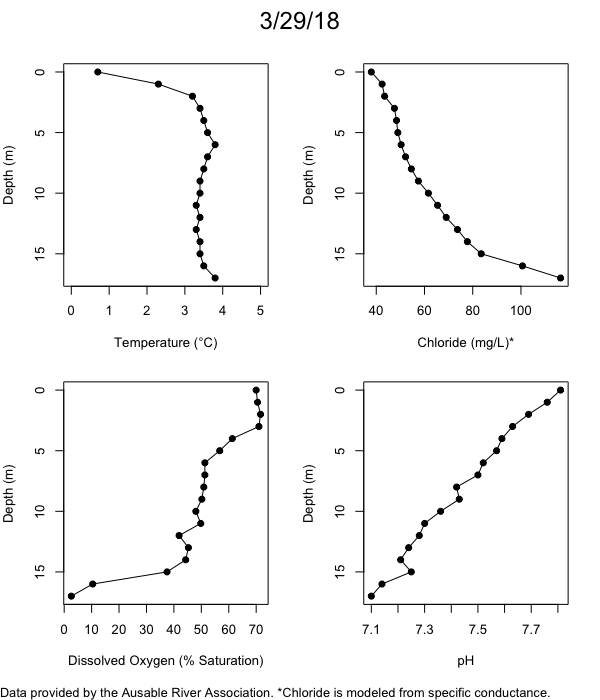
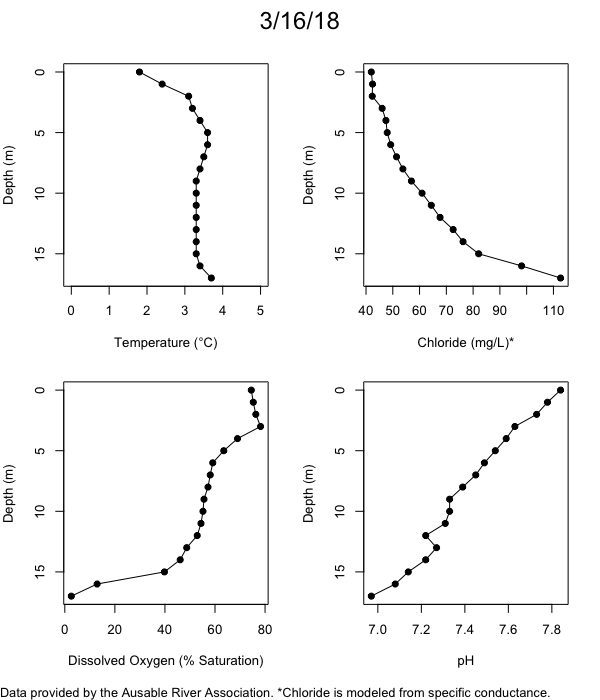
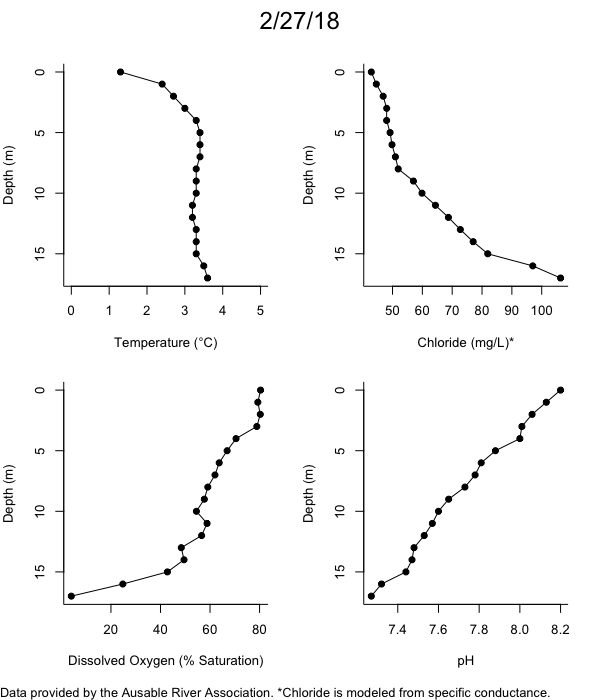
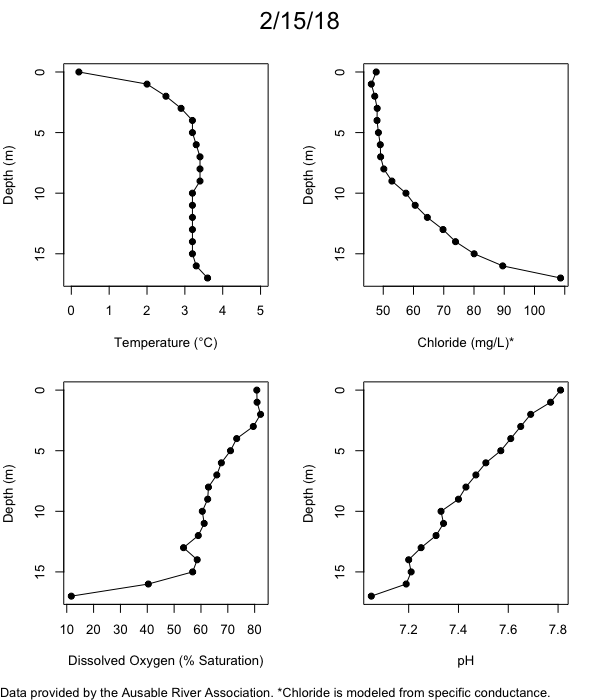
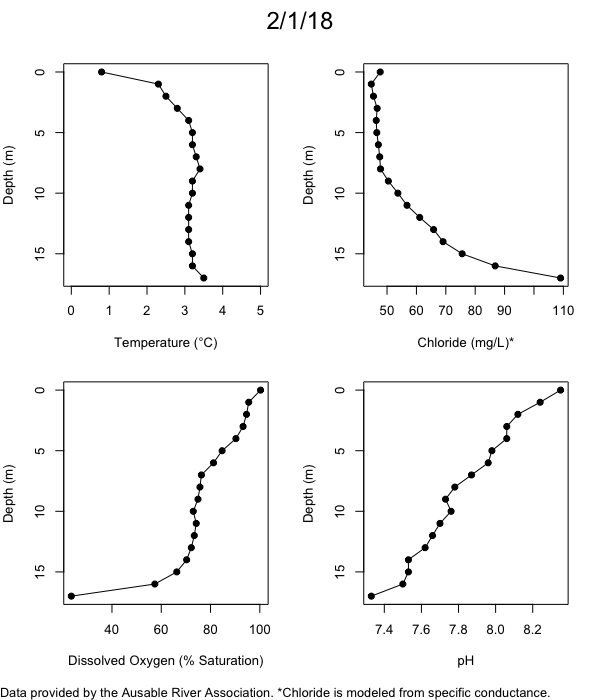
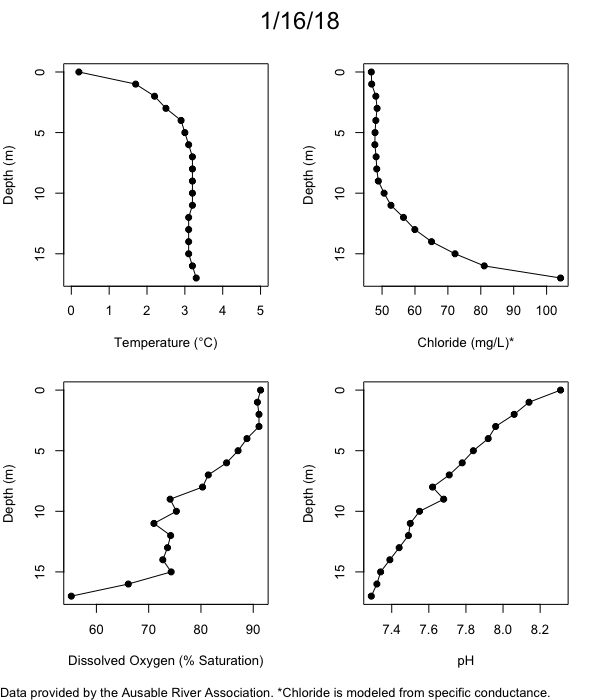
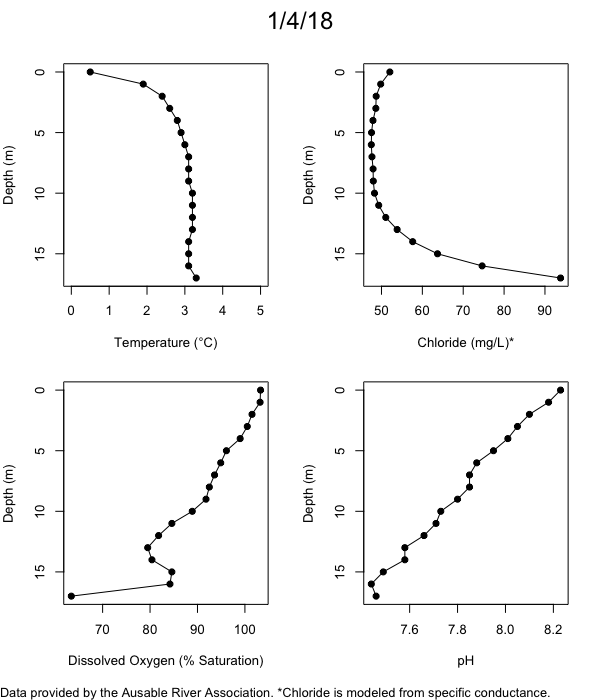
Below are heatmap plots showing temperature, dissolved oxygen, and chloride data through our most recent sampling visit. AFC staff sample Mirror Lake on a bi-weekly basis during the open water season and monthly during the winter. Annually we publish a detailed report on the water quality of Mirror Lake. This work is done in close partnership with the Adirondack Watershed Institute.
How to read the plots below: The plots below depict changes in the measured parameter over both space (through the water column) and time. The x-axis is time, looking across the plot from left to right gives a sense of how the lake has changed over time. The y-axis is depth in the water column, the top of the plot is the surface of the lake and the bottom of the plot is the bottom of the lake. The colors inside the plot represent the values for the parameter being plotted, a key is on the right side of the plot.
Mirror Lake Temperature
The surface water temperature in 2018 was warmer than in past years. Additionally, thermal stratification was stronger.

View an interactive temperature plot.
Mirror Lake Dissolved Oxygen
Mirror Lake has experienced hypoxic conditions (<2 mg/L) at the lake bottom in 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019. In 2017, 2018, and 2019 the size and duration of the hypoxic zone was both larger and longer than in 2016. Understanding the extent, duration, and cause of hypoxia is important to maintaining the health of many aquatic organisms, including fish.

View an interactive dissolved oxygen plot.
Mirror Lake Chloride
Road salt is one of the major threats to Mirror Lake. Stormwater directly enters the lake from over 20 outfalls around the shore. When this salt-laden runoff enters the lake it settles to the bottom. This can be observed during each winter. That build-up of salt persists through the summer if the lake does not turn over in the spring, this phenomenon occurred in 2019, 2018, 2017, and we expect it also occurred in 2015. The lack of turnover exacerbates the hypoxic conditions mentioned above, threatening the fish and other organisms living in the lake. Our recent scientific peer-reviewed paper linked the lack of spring turnover to the buildup of salt at the bottom of the lake.

View an interactive chloride plot.
Mirror Lake Conditions
Funding for this work is provided by the New York State Department of State, Cloudsplitter Foundation, Village of Lake Placid, Town of North Elba, IRONMAN Foundation, Mirror Lake Watershed Association, and Golden Arrow Lakeside Resort. For more information on our work on Mirror Lake email : contactus@ausablecenter.org.